AB PSYCH 2
tagPsychology
tagAbnormal Psychology
added by -
nglmrrz
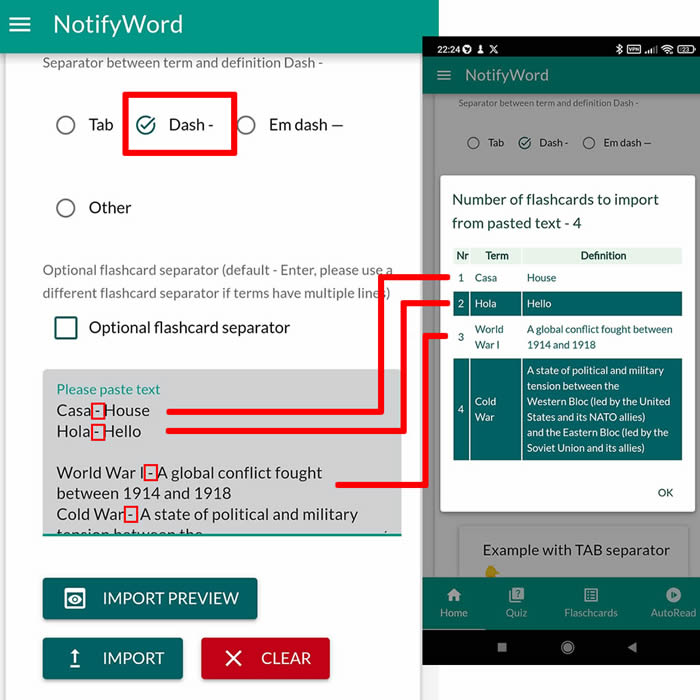
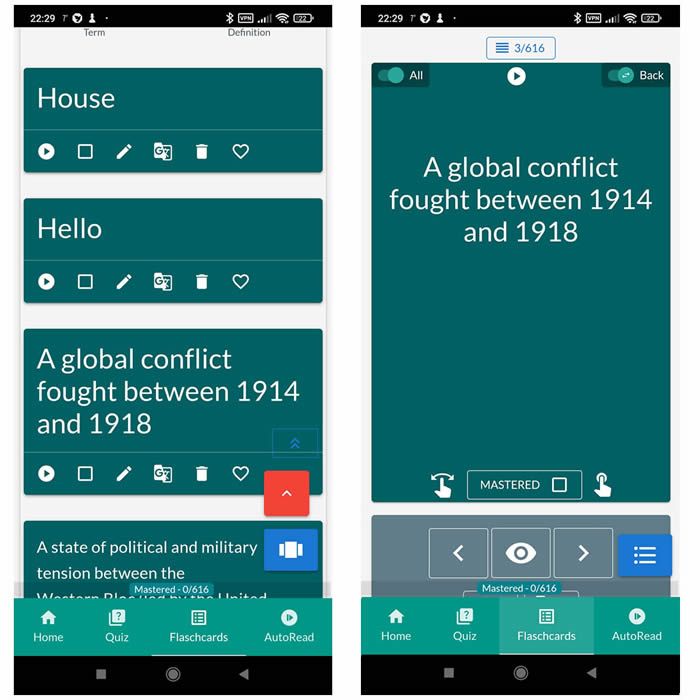
On the website, you create flashcards, which you then import into the Android NotifyWord app in the 'Import' section. To generate flashcards from commands or image, pictures, you can use external AI applications, such as ChatGPT. The flashcards require the Android app, which offers interactive features and AUTOLEARN — background learning.
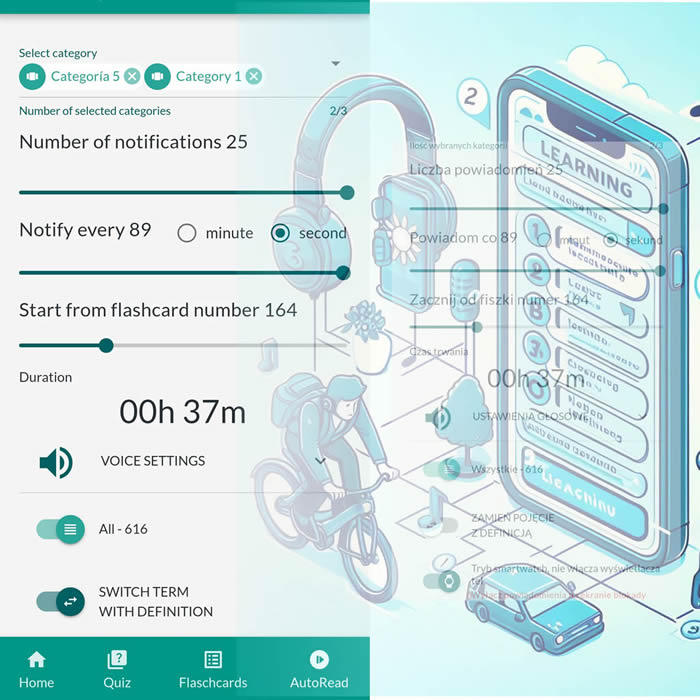
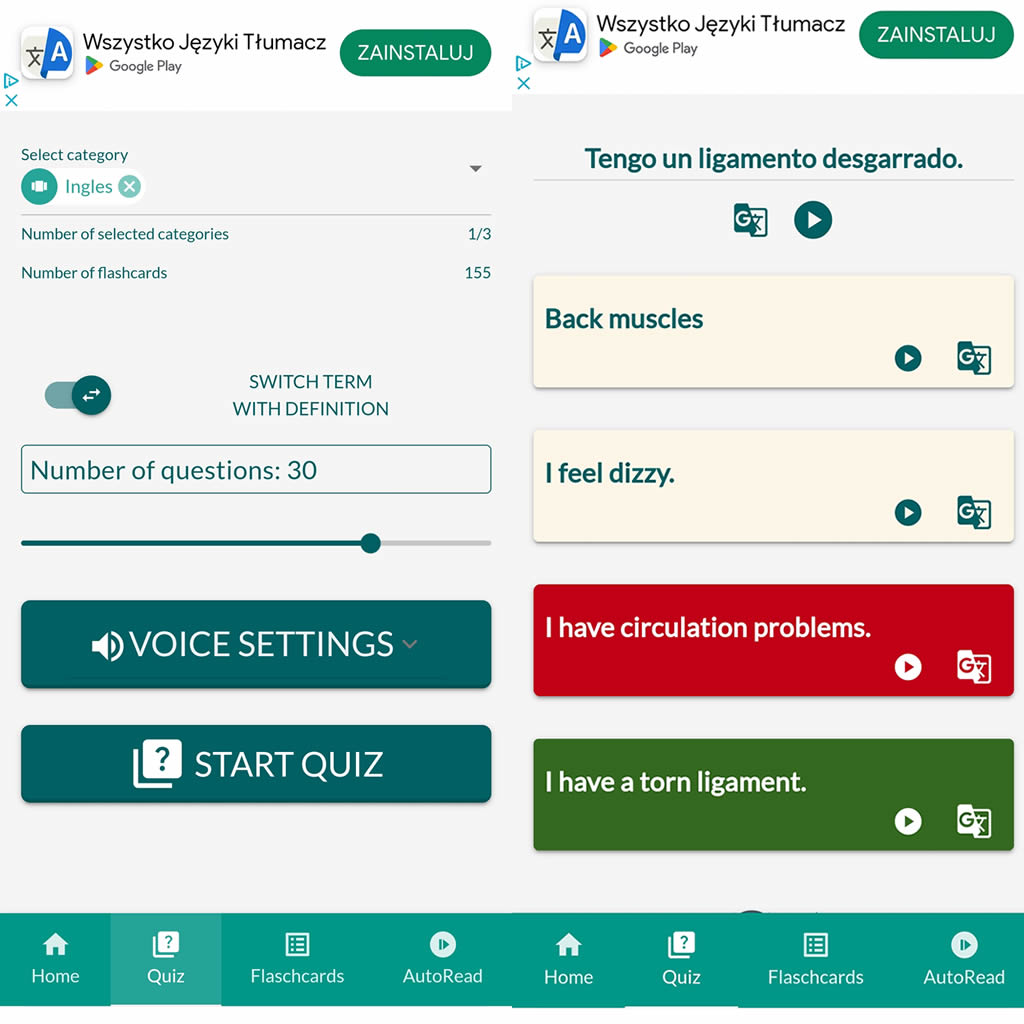
🤖📚📖❓🎧🚴 Voice flashcards - an Android app for learning without touching the phone.
➕ On the website, you can create your own sets of flashcards, both public and private, import them from text, and then import them into the Android application.
| Term/Front | Definition/Back |
|---|---|
|
1 A conceptual approach Could mean an emphasis on a specific cause of abnormal behavior Problems occur when information from other areas is ignored |
One-Dimensional Models (Single Paradigm) |
|
2 Interdisciplinary, eclectic, and integrative “System” of influences that cause and maintain suffering Draws upon information from several sources View abnormal behavior as multiply determined |
Multidimensional Models (draws from multiple paradigms) |
| 3 Refers to the genetic code of the individual. This is all the information that is found inside the individual's cells. | Genotype |
| 4 Is the expression of the genotype that is visible to other people and can be observed. | Phenotype |
| 5 The role of the nervous system in disease and behavior |
The Field of Neuroscience |
| 6 Brain and spinal cord |
The Central Nervous System (CNS) |
| 7 Somatic and autonomic branches |
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) |
| 8 Cell body | Soma |
| 9 Branches that receive messages from other neurons |
Dendrites |
| 10 Trunk of neuron that sends messages to other neurons |
Axon |
| 11 Buds at end of axon from which chemical messages are sent |
Axon Terminals |
| 12 Small gaps that separate neurons |
Synapses |
| 13 the chemical messengers | Neurotransmitters |
| 14 Regulates behaviors, moods, thoughts |
Serotonin |
| 15 Reduces postsynaptic activity, which inhibits behavior and emotions |
Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and benzodiazepines |
| 16 block receptors of norepinephrine reduces Arousal & anxiety | Norepinephrine and beta blockers |
| 17 Schizophrenia by blocking receptors (lowers Dop) | Dopamine |
| 18 Heart rate, blood pressure, respiration |
Medulla |
| 19 Regulates sleep stages |
Pons |
| 20 Involved in physical coordination |
Cerebellum |
|
21 Coordinates movement with sensory input Contains parts of the reticular activating system (RAS) |
Midbrain |
| 22 Receives and integrates sensory information |
Thalamus |
|
23 Controls eating, drinking, aggression, sexual activity Regulates emotions and expressions |
Hypothalamus |
|
24 Location of most sensory, emotional, and cognitive processing Two specialized hemispheres (left and right) joined by the corpus callosum |
Forebrain (Cerebral Cortex) |
| 25 Controls voluntary muscles and movement |
Somatic Branch of PNS |
|
26 Sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the ANS Regulates cardiovascular system & body temperature Also regulates the endocrine system and aids in digestion |
Autonomic Branch of the PNS |
| 27 Hormones |
The Endocrine System |
| 28 Influence the form and expression of normal and abnormal behavior |
Cultural Factors |
| 29 Exerts a strong and puzzling effect on psychopathology |
Gender Effects |
|
30 Addresses developmental changes Such changes influence and constrain what is normal and abnormal |
Life-Span Developmental Perspective |
|
31 Several paths to a given outcome Paths may operate differentially at different developmental stages |
Equifinality |
| 32 Is the rule, not the exception in explaining normal and abnormal behavior |
Multiple Causation |
| 33 studies disorders within context of normal child development |
Developmental Psychopathology |
| 34 impairment on the brain's development of neurological pathways that influence performance or functioning | Neurodevelopmental Disorders |
|
35 group of disorders that are linked by varying difficulties in controlling aggressive behaviors, self-control, and impulses |
Disruptive, Impulse Control and Conduct Disorder |
|
36 Characterized by outward-directed behaviors. Common characteristics: Noncompliance, aggressiveness, overactivity, impulsiveness. |
Externalizing Disorders |
|
37 Characterized by inward-focused behaviors Common characteristics: Depression, anxiety, social withdrawal. |
Internalizing Disorder |
|
38 Excessive levels of activity Distractibility and difficulty concentrating May have difficulty with peer interactions |
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder |
| 39 More aggressive, acting out, antisocial parents, family hostility |
Conduct Disorder |
|
40 More off-task behavior, cognitive and achievement deficits |
ADHD |
| 41 Pattern of engaging in behaviors that violate social norms and the rights of others, and are often illegal | Conduct Disorder |
| 42 recurrent verbal or physical aggressive outbursts that are out of proportion to the circumstances | Intermittent explosive disorder |
|
43 behaviors do not meet criteria for CD (especially extreme physical aggressiveness) but child displays pattern of defiant behavior Argumentative, loses temper, lack of compliance, deliberately aggravates others, hostile, vindictive, spiteful, or touchy, blames others for own problems |
Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) |
| 44 To form identical twins, one fertilised egg (ovum) splits and develops into two babies with exactly the same genetic information | Monozygotic twins |
| 45 To form fraternal, two eggs (ova) are fertilised by two sperm and produce two genetically unique children | Dizygotic twins |
| 46 persistent pattern of antisocial behavior | Life course |
|
47 Maturity gap between physical maturation and rewarding adult behaviors |
Adolescence-Limited |
| 48 high negative affect, low positive affect |
Depression |
| 49 high negative affect but not low levels of positive affect | Anxiety |
|
50 Fears and worries common in childhood More severe and persistent worry Must interfere with functioning |
Anxiety |
|
51 Worry about parental or personal safety when away from parents Typically first observed when child begins school |
Separation anxiety disorder |
|
52 Extremely shy and quiet May exhibit selective mutism Refusal to speak in unfamiliar social setting |
Social anxiety disorder |
|
53 Exposure to trauma - Chronic physical or sexual abuse, Community violence, Natural disasters Symptom categories - Flashbacks, nightmares, intrusive thoughts, Avoidance, Negative cognitions and moods, Hyperarousal and vigilance May exhibit agitation instead of fear or hopelessness |
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) |
|
54 Contamination from dirt and germs Aggression Thoughts about sex and religion more common in adolescence |
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) |
| 55 Evidence of inadequate development in a specific area of academic, language, speech or motor skills |
Learning Disability |
|
56 Difficulties in learning basic academic skills (reading, mathematics, or writing) inconsistent with person’s age, schooling, and intelligence Significant interference with academic achievement or activities of daily living |
Specific Learning Disorder |
| 57 formerly called reading disorder, involves significant difficulty with word recognition, reading comprehension, and typically written spelling as well | Dyslexia |
| 58 formerly called mathematics disorder, involves difficulty in producing or understanding numbers, quantities, basic arithmetic operations | Dyscalculia |
| 59 formerly called phonological disorder, involves correct comprehension and sufficient vocabulary use, but unclear speech and improper articulation | Speech Sound Disorder |
| 60 stuttering, is a disturbance in verbal fluency that is characterized by one or more of the following speech patterns: frequent repetitions or prolongation of sounds | Childhood onset fluency disorder |
| 61 involves one or more vocal and multiple motor tics (sudden, rapid movement or vocalization) that start before the age of 18 | Tourette's disorder |
| 62 formerly called motor skills disorder, involves marked impairment in the development of motor coordination that is not explainable by intellectual disability or a disorder such as cerebral palsy | Developmental coordination disorder |
| 63 involves seemingly purposeless movements repeated over and over that interfere with functioning and could even cause self-injury | Stereotypic movement disorder |
| 64 Formerly called mental retardation, characterized by significant limitations both in intellectual functioning and in adaptive behavior as expressed in conceptual, social, and practical adaptive skills |
Intellectual Disability (Intellectual Developmental Disorder) |
|
65 Asperger’s disorder, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified, and childhood disintegrative disorder Share similar features, vary only in severity Specifiers include with or without accompanying intellectual impairment, language impairment, or catatonia Pay attention to different parts of faces than do people without autism; focus on mouth, neglect eye region Crucial for understanding and successfully engaging in social interactions Echolalia Pronoun reversal Become extremely upset when routine is altered |
Autism Spectrum Disorder |
| 66 immediate or delayed repeating of what was heard |
Echolalia |
| 67 refer to themselves as “he” or “she” |
Pronoun reversal |
ℹ️ On the website, you create flashcards, which you then import into the Android NotifyWord app in the 'Import' section. To generate flashcards from commands or image, pictures, you can use external AI applications, such as ChatGPT. The flashcards require the Android app, which offers interactive features and AUTOLEARN — background learning.☝️
📚✍️📲 You can copy the flashcards to your set, copy the flashcards and paste them in the import tab by selecting the TAB separator.